Welcome to our comprehensive beginner’s guide on altcoins. If you’ve heard about cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, you might be curious about the other digital currencies out there. This guide will explain what altcoins are, how they work, and the role they play in the cryptocurrency market. Our goal is to help you understand altcoins and explore their potential in a clear, engaging, and accurate way. So, let’s dive into the world of altcoins.
Contents
What are Altcoins?
Altcoins, short for “alternative coins,” are cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin. They were created following the success of Bitcoin, aiming to improve upon or offer different features and use cases. With thousands of altcoins in existence, they provide diversity and options for investors and users within the cryptocurrency market.
Altcoins are often designed to address perceived limitations or shortcomings in Bitcoin, such as transaction speed, energy consumption, or privacy. They may also cater to specific industries, applications, or market niches, enabling a wide range of functionalities beyond Bitcoin’s original scope as a digital currency. This has led to the development of various ecosystems, platforms, and services, all built around these alternative cryptocurrencies.
Some well-known examples of altcoins include Ethereum, which introduced the concept of smart contracts and supports decentralized applications (dApps), and Litecoin, which aimed to improve upon Bitcoin’s transaction speed and reduce energy consumption. The sheer variety of altcoins means there’s likely a digital currency out there tailored to a specific use case or offering unique advantages.
It is essential to note that not all altcoins succeed in gaining traction or achieving their goals, and some may eventually become obsolete or fail. As with any investment, it is crucial to conduct thorough research and assess the potential risks and rewards before investing in altcoins.
How Altcoins Work
Like Bitcoin, altcoins use blockchain technology to record and verify transactions. However, they may have different consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS) or Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), compared to Bitcoin’s Proof of Work (PoW) system.
Key aspects of altcoins include:
- Cryptography: Ensures secure transactions and prevents counterfeiting.
- Decentralization: Operates on a peer-to-peer network, without a central authority.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Determines how the network validates transactions and maintains security.
Consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in the functioning of a blockchain network. They are responsible for ensuring that all nodes (computers) in the network agree on the contents of the blockchain. This process is essential for maintaining the integrity and security of the distributed ledger.
Different consensus mechanisms include:
Proof of Work (PoW): PoW requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. Bitcoin and many early altcoins use this consensus mechanism. While secure, PoW is energy-intensive and has raised concerns about its environmental impact.
Proof of Stake (PoS): PoS is an alternative consensus mechanism that selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold (their stake) and other factors. Validators are chosen to create new blocks and validate transactions, reducing the energy consumption associated with PoW. Examples of altcoins using PoS include Ethereum (with its upcoming transition to Ethereum 2.0) and Cardano.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): DPoS is a variation of PoS, where token holders vote for a limited number of delegates who validate transactions and create new blocks. This system aims to provide more efficient and democratic governance. Examples of altcoins using DPoS include EOS and Lisk.
Proof of Authority (PoA): PoA relies on a pre-selected group of trusted validators who are authorized to validate transactions and create new blocks. This consensus mechanism is designed for private or permissioned blockchains, where the participating nodes are known and trusted. PoA is faster and more energy-efficient than PoW but sacrifices decentralization.
History of Altcoins
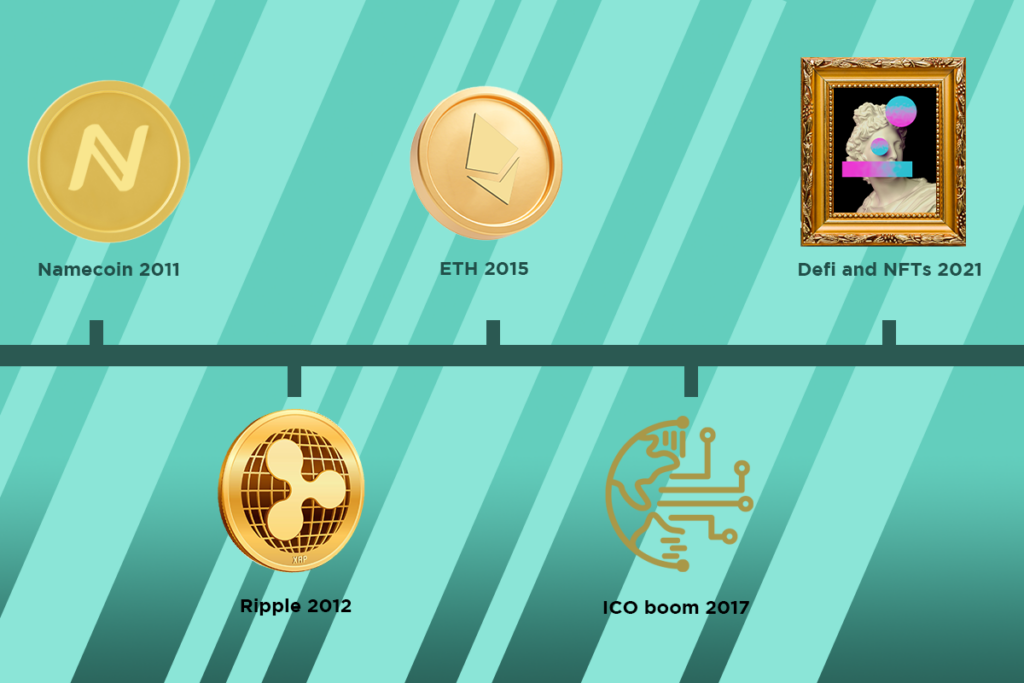
Altcoins emerged in the cryptocurrency market after Bitcoin’s success. The first altcoin, Namecoin, was created in 2011, aiming to improve domain name registration using blockchain technology. Since then, thousands of altcoins have been introduced, each addressing various challenges or targeting specific use cases.
Key events in altcoin history:
- 2011: Namecoin, the first altcoin, is launched.
- 2012: Ripple (XRP) is created, focusing on facilitating international money transfers.
- 2015: Ethereum is launched, introducing smart contracts and enabling the creation of decentralized applications (dApps).
- 2017: The Initial Coin Offering (ICO) boom results in hundreds of new altcoins entering the market.
- 2020-2021: Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) drive further growth in the altcoin space.
The Different Types of Altcoins
There are several types of altcoins, each with its unique features and uses. Some common types include:
- Platform Tokens: Provide a platform for creating and managing decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts, e.g., Ethereum.
- Privacy Coins: Focus on anonymous and private transactions, e.g., Monero and Zcash.
- Stablecoins: Pegged to a stable asset like fiat currency or gold, aiming to reduce price volatility, e.g., Tether and USD Coin.
- Utility Tokens: Grant access to a specific product, service, or platform, e.g., Binance Coin and Chainlink.
- Exchange-specific Tokens: Issued by cryptocurrency exchanges to offer discounts or rewards, e.g., KuCoin Shares.
Pros and Cons of Altcoins
There are now hundreds of altcoins launched almost daily, all offering different key features as compared to bitcoin. With thousands of altcoins now on the market, there are several pros and cons to them, see some examples below:
Pros:
- Innovation: Altcoins introduce new features and improvements over Bitcoin, driving technological advancements.
- Investment Opportunities: Potential for high returns in a growing market.
- Diversification: A wide range of altcoins offers investment diversification options.
Cons:
- Volatility: Altcoins can experience significant price fluctuations, posing risks to investors.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments are still developing regulations for cryptocurrencies, which can impact altcoin markets.
- Scams and Fraud: Some altcoins may be fraudulent or have weak security measures, putting investments at risk.
How to Choose an Altcoin

Selecting the right altcoin for your investment or use case requires careful consideration. Here are some factors to consider:
- Project Vision: Understand the altcoin’s goals and how it aims to achieve them.
- Use Case: Determine if the altcoin has a viable real-world application or solves an existing problem.
- Technology: Assess the underlying technology and its potential for scalability, security, and efficiency.
- Team: Evaluate the team’s experience, expertise, and past achievements in the blockchain and cryptocurrency industries.
- Community: Gauge the size and engagement of the project’s community, as a strong community often indicates support and potential adoption.
- Partnerships: Identify any strategic partnerships that may drive adoption or contribute to the project’s success.
Tips for Investing in Altcoins
As with any lower market cap cryptocurrency, there are various things to consider before investing in altcoins. As a general rule of thumb, altcoins are often subject to high price volatility, which can often result in substantial gains and losses. Before investing in altcoins you should do as much research as possible. Some things to consider:
- Research: Thoroughly investigate the altcoin’s project, team, and technology before investing.
- Diversification: Spread your investments across multiple altcoins to mitigate risk.
- Risk Management: Only invest what you can afford to lose and consider using stop-loss orders.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with industry news, developments, and trends to make informed decisions.
- Long-term Perspective: Be prepared for market volatility and consider a long-term investment strategy.
Storage: Wallet Options
Once you own altcoins, it’s crucial to store them securely. There are various wallet options available, each with its pros and cons:
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices that store your private keys offline, providing high security. Examples include Ledger and Trezor.
- Software Wallets: Applications installed on your computer or smartphone that store your private keys. Examples include Metamask and Trust Wallet.
- Paper Wallets: Printed documents containing your public and private keys, which must be stored securely.
- Web Wallets: Online wallets accessible through a web browser, often provided by cryptocurrency exchanges. Note that these wallets may have lower security due to being constantly connected to the internet.
Conclusion
Altcoins represent a diverse and innovative aspect of the cryptocurrency market, offering alternative investment opportunities and use cases. While they carry potential risks and challenges, understanding their unique features and staying informed can help you make the most of this growing market. We hope this beginner’s guide to altcoins has provided you with valuable insights and a solid foundation for exploring the world of alternative cryptocurrencies.
Remember, this guide is meant to serve as an introduction to altcoins. As you dive deeper into the world of cryptocurrencies, always conduct thorough research and stay updated on the latest developments. Happy exploring 🙂


![Top VIP Crypto Casinos with High Roller Perks [2025]](https://coinnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/cbf67059-de4a-485a-b7cc-603b861d1eef-e1748341865818.png)