Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that allows developers to create and run decentralized applications, or dapps, on the Ethereum network. In this guide, we’ll explore the basics of Ethereum, including its history, how it works, how it differs from Bitcoin, and what role gas plays in Ethereum transactions.
In this guide, we’ll cover the basics of Ethereum and it’s adapted uses since its launch in 2015.
A Brief History of Ethereum
Ethereum was first proposed in late 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, a Russian-Canadian programmer and writer. Buterin was inspired by Bitcoin’s potential to be more than just a digital currency and sought to build a platform that could support the creation of decentralized applications. Buterin published the Ethereum whitepaper in 2014, outlining the architecture and potential use cases of the platform.

In 2015, the Ethereum network launched, and the first block was mined on July 30, 2015. The launch was not without its challenges, however. A few weeks after the launch, a bug in the Ethereum code led to the theft of more than 3.6 million Ether, which was then worth around $50 million.
Despite this setback, Ethereum continued to grow, and by early 2016, it had become the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, behind only Bitcoin. In 2017, the price of Ether skyrocketed, reaching a (then) all time high of just over $1,386.
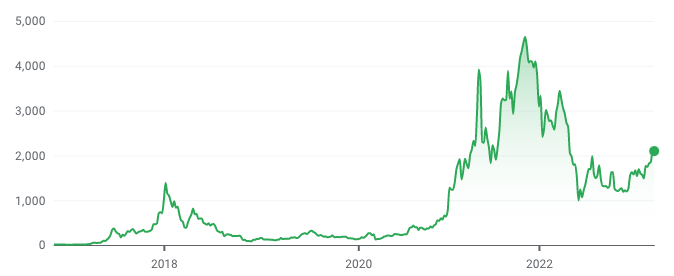
In 2021, the price of Ethereum hit new record levels, rising from under $1,000 to an impressive all time high of $4,664.
How Does Ethereum Work?
Ethereum is built on blockchain technology, just like Bitcoin. However, there are a few key differences between the two. While Bitcoin is primarily a digital currency, Ethereum is a platform that allows developers to create and run decentralized applications. Here are a few key features of Ethereum:
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. Smart contracts allow for automated transactions and eliminate the need for intermediaries.
- Decentralized Applications (dapps): Decentralized applications, or dapps, are applications that run on the Ethereum network. These applications are built on smart contracts and can be used for a wide range of purposes, from gaming to finance to social networking.
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a virtual machine that executes code on the Ethereum network. It’s responsible for running smart contracts and executing transactions on the network.
How Does Ethereum Compare to Bitcoin?
While Ethereum and Bitcoin are both built on blockchain technology, they have some key differences. Here are a few of the main ways that Ethereum differs from Bitcoin:
- Purpose: While Bitcoin is primarily a digital currency, Ethereum is a platform for creating and running decentralized applications.
- Mining Algorithm: Ethereum uses a different mining algorithm than Bitcoin. While Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 algorithm, Ethereum uses the Ethash algorithm.
- Block Time: Ethereum has a faster block time than Bitcoin. Ethereum blocks are created every 15 seconds, while Bitcoin blocks are created every 10 minutes.
Ethereum’s Gas Cost
In order to use Ethereum, users must pay a fee for each transaction made on the platform. This fee is known as “gas,” and it is used to compensate the network’s miners for the work they do to verify transactions and maintain the network.
Read our guide to Ethereum Gas here.
Gas is calculated based on the complexity of the transaction being made. For example, sending Ether to another user requires a relatively simple transaction and, therefore, a lower gas cost, while executing a smart contract requires a more complex transaction and, therefore, a higher gas cost.
Users set the gas price they are willing to pay per unit of gas, and this price is used to determine the total cost of the transaction. If the gas limit is exceeded, the transaction will fail, and the user will lose the gas they paid for the failed transaction.
Advantages of Ethereum
Ethereum’s blockchain platform offers several advantages, including:
- Smart contracts: Smart contracts allow for the creation of decentralized applications that can automate tasks without the need for intermediaries.
- Decentralization: Ethereum is decentralized, meaning that it operates without a central authority, making it more resistant to censorship and other types of attacks.
- Flexibility: Ethereum’s programming language, Solidity, allows developers to build a wide range of applications, from simple games to complex financial instruments.
- Transparency: All transactions made on the Ethereum network are publicly visible on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Conclusion
In summary, Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that enables developers to build and run decentralized applications. It differs from Bitcoin in several ways, including its focus on smart contracts and dapps, its use of gas for transactions, and its mining algorithm. By understanding the basics of Ethereum, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the potential of blockchain technology and the role that Ethereum plays in the wider cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Ethereum has come a long way since its launch in 2015, and it has continued to evolve and grow. As more developers build decentralized applications on the Ethereum platform and more users participate in the network, the potential of Ethereum as a transformative technology becomes more and more clear. While there are still many challenges and obstacles to overcome, the future of Ethereum looks bright, and it will undoubtedly continue to shape the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology for years to come.








